Oscar Martinez Mozos
Research
- Research topics:
- Tracing of commodities in daily human life.
- Object Detection and Categorization in 3D Point Clouds.
- People Detection.
- Semantic Categorization of Places.
- Interest Point Detectors and Local Descriptors for Visual SLAM.
- Spatial Patterns of Neural Cells.
- Biosignal Analysis.
- List of projects.
Tracing of commodities indoors in daily human life
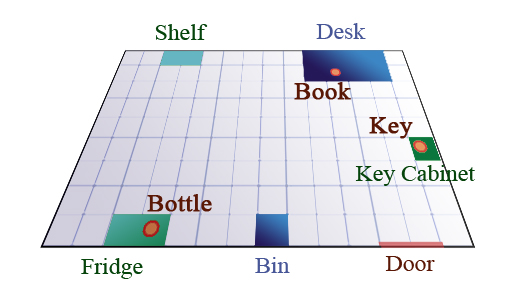
Daily life assistance for elderly people is one of the most promising scenarios for service robots in the near future. In particular, the go-and-fetch task will be one of the most demanding tasks in these cases. We work on an informationally structured room that supports a service robot in the task of daily object fetching.
Related Publications:
- O. M. Mozos, F. Chollet, K. Murakami, K. Morooka, T. Tsuji, R. Kurazume, and
T. Hasegawa,
Tracing commodities in indoor environments for service robotics,
in Proc. of the 10th IFAC Symposium on Robot Control, vol. 10, (Dubrovnik, Croatia), September 2012. [ bib ]
Object Detection and Categorization in 3D Point Clouds
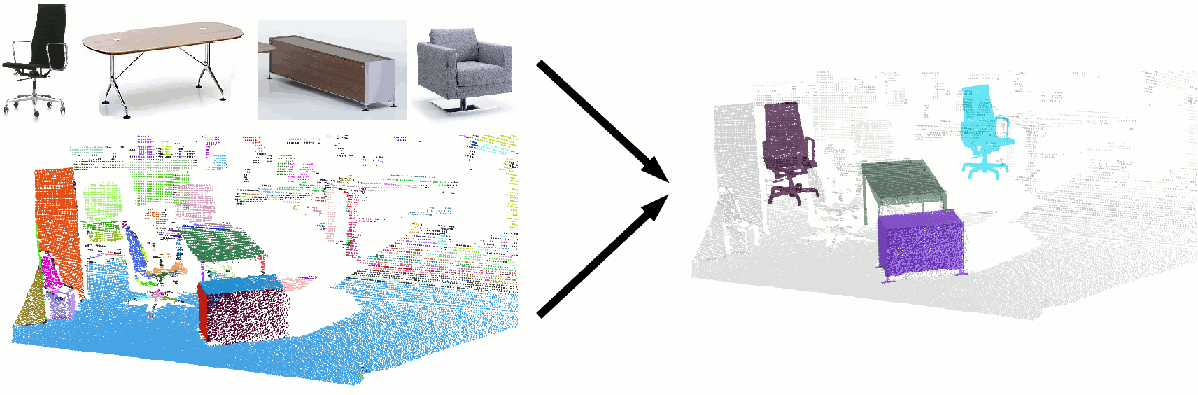
We work on several approaches to detect and categorize different furniture objects like chairs, tables or sideboards in 3D point clouds in the presence of clutter and occlusion. The detection and categorization of these objects is an important capability for service robots acting in indoor environments, as they play important roles in the tasks to be performed by these robots.
Collaborators:
- Intelligent Autonomous Systems Group, Technische Universitaet Muenchen (TUM), Germany.
- ROS.org package for furniture classification using the Kinect camera.
Related Publications:
- O. M. Mozos, Z.-C. Marton, and M. Beetz,
Furniture models learned from the WWW - using web catalogs to locate and categorize unknown furniture pieces in 3D laser scans,
IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, vol. 18, pp. 22 - 32, June 2011. [ bib | online | DOI | .pdf ]
People Detection in Range Data
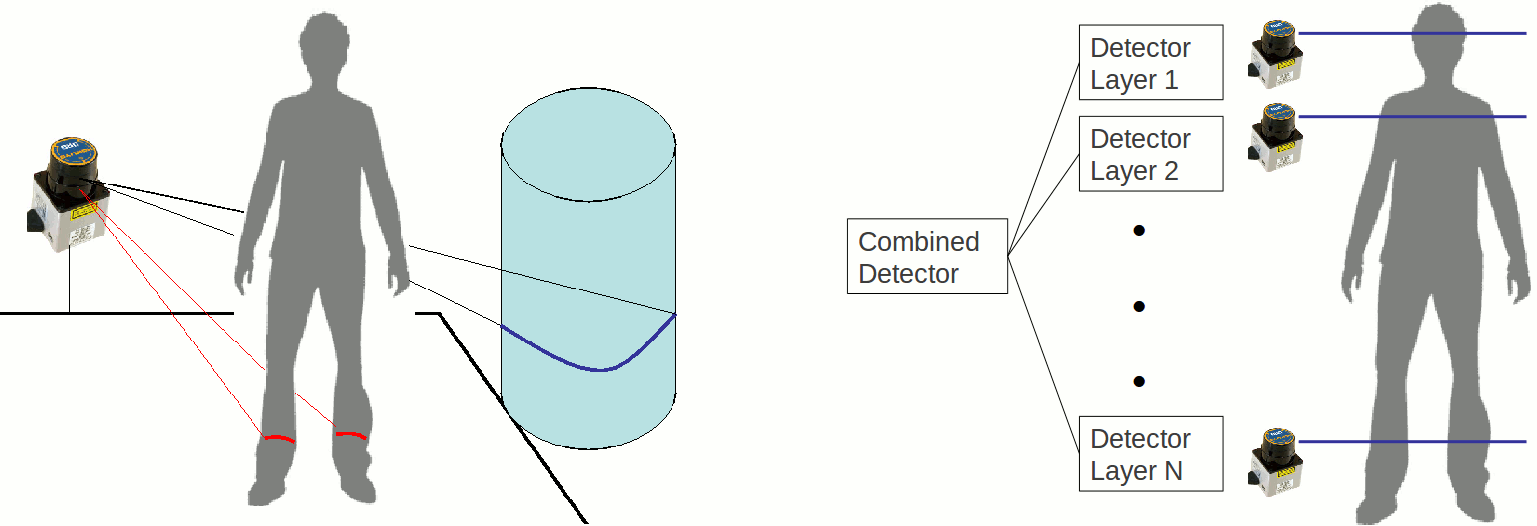
The recognition of people is key a capacity for service robots that interact with humans. We work on the detection of people with laser scans using one or several layers. The key idea is to learn classifiers for body parts that are represented by segments in laser scans. The main goal is to obtain a robust classifier which is able to detect people in different environments.
One layer detection
- Office environment (joint work with Kai O. Arras): [avi: 918k].
- Video experiment "Scenario 1": [avi: 925k].
- Video experiment "Scenario 1": [mp4: 2619k].
- Video experiment "Scenario 2": [avi: 1499k].
- Video experiment "Scenario 2": [mp4: 4219k].
- Video experiment "Scenario 3": [avi: 902k].
- Video experiment "Scenario 3": [mp4: 2213k].
- ROS package for people detection using range data. Available at the public tum-ros repository under perception/people_detector_node/.
- K. O. Arras and O. M. Mozos, eds., Special issue on people detection and tracking, vol. 2. International Journal of Social Robotics, March 2010. [ bib | online ]
-
O. M. Mozos, R. Kurazume, and T. Hasegawa,
Multi-part people detection using 2D range data,
International Journal of Social Robotics, vol. 2, pp. 31-40, March 2010. [ bib | online | DOI | more details | .pdf ] -
K. O. Arras, O. M. Mozos, and W. Burgard,
Using boosted features for the detection of people in 2D range data,
in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 3402-3407, April 2007. [ bib | video | more details | .pdf ]
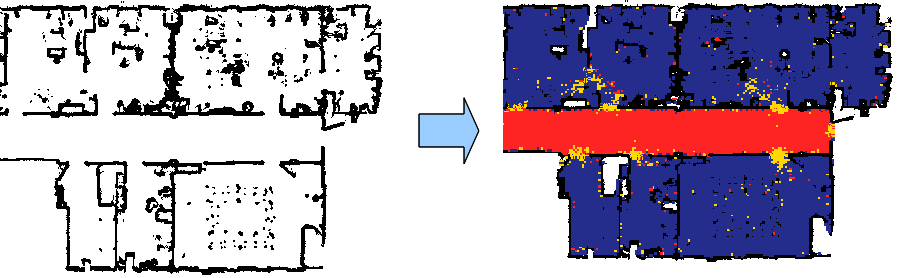
Semantic Categorization of Places
 |
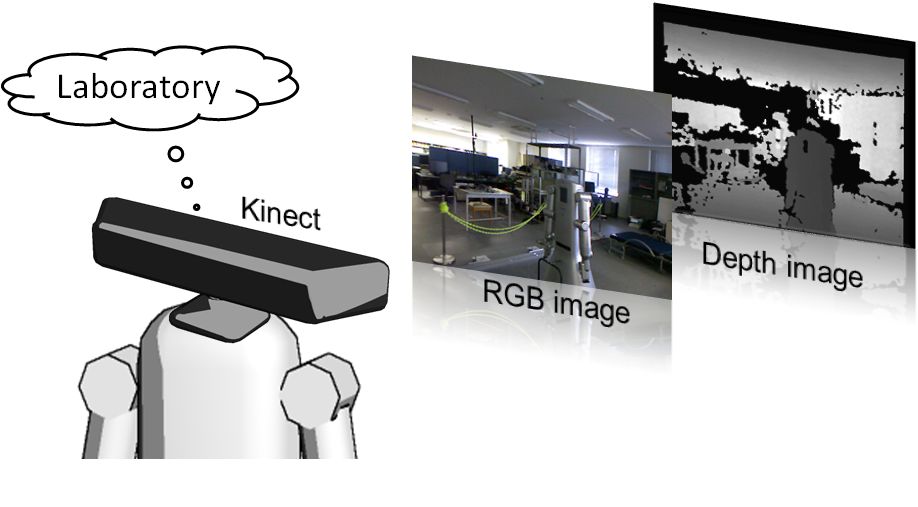 |
Semantic labeling is the problem of assigning labels with semantic meaning to the different places that composed indoor environments. Typical labels include "corridor", "room", "office", "lab", or "doorway". The ability to learn such semantic categories from sensor data enables a mobile robot to extend the representation of the environment facilitating the interaction with humans. We study different approach to categorize places using as input different sensors such as laser scans, vision cameras, RGB-D cameras.
- Data sets corresponding to the semantic classifications of places in different indoor environments using 2D laser scans.
- Data sets corresponding to the semantic classifications of places in different indoor environments using RGB-D sensors (Kinect camera).
- Online labeling for three classes using laser scans only: [avi: 77k].
- Online labeling for six classes using laser scans and images (joint work with Axel Rottmann): [avi: 470k].
- O. M. Mozos, H. Mizutani, R. Kurazume, and T. Hasegawa,
Categorization of indoor places using the kinect sensor,
Sensors, vol. 12, pp. 6695-6711, May 2012. [ bib | online | DOI | datasets | .pdf ] -
A. Pronobis, O. M. Mozos, B. Caputo, and P. Jensfelt,
Multi-modal semantic place classification,
International Journal of Robotics Research, vol. 29, pp. 298-320, February-March 2010. [ bib | online | DOI ] -
O. M. Mozos, Semantic Place Labeling with Mobile Robots.
Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics (STAR), Germany: Springer, 2010.
[ bib |
online ]

Interest Point Detectors and Local Descriptors for Visual SLAM
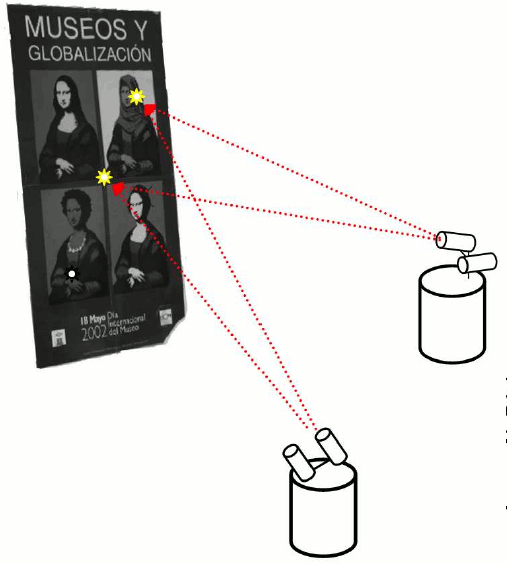
Acquiring maps of the environment is a fundamental task for autonomous mobile robots, since the maps are required in higher level tasks, such as navigation and localization. In consequence, the problem of simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) has received significant attention in the robotics community. If the robot uses a camera as sensor for constructing the map, then this approach is known as visual SLAM.
We compare the behavior of different interest points detectors and descriptors under the conditions needed to be used as landmarks in vision-based simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM).
Collaborators:
- Automation, Robotics and Computer Vision lab (ARCV), the Miguel Hernandez University.
-
A. Gil, O. M. Mozos, M. Ballesta, and O. Reinoso,
A comparative evaluation of interest point detectors and local descriptors for visual SLAM,
Machine Vision and Applications (MVA), vol. 21, pp. 905-920, October 2010. [ bib | online | DOI | .pdf ] -
A. Gil, O. Reinoso, W. Burgard, C. Stachniss, and O. M. Mozos,
Improving data association in rao-blackwellized visual SLAM,
in Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), (Beijing, China), pp. 2076-2081, 2006. [ bib | .pdf ]
Spatial Patterns of Neural Cells
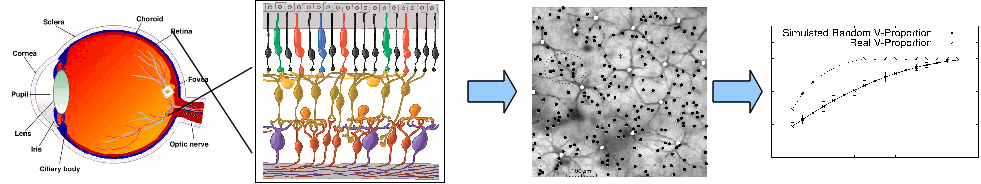
There exist several attempts to develop bio-inspired artificial retinas with the purpose of replacing or partially recovering damaged functionalities in perception. Moreover, retinal-inspired models have been used to improve the vision system in robots. However, the complete information process inside the retina is not fully understood yet.
The retina is organized into layers formed by many local neuronal circuits which work in parallel. The study of the spatial relations between these mosaics is highly relevant to understand how the visual information spreads along them.
We apply spatial point patterns methods to study the spatial relations between the different mosaics in the retina.
- Retinal mosaics data sets.
Collaborators:
- Bioengineering Institute, Miguel Hernandez University, Spain.
- Dept. of Physiology, Medical University of Vienna, Austria.
-
O. M. Mozos, J. A. Bolea, J. M. Ferrandez, P. K. Ahnelt, and E. Fernandez,
V-Proportion: A method based on the Voronoi diagram to study spatial relations in neuronal mosaics of the retina,
Neurocomputing, vol. 74, pp. 418-427, December 2010. [ bib | online | DOI | datasets | .pdf ] -
P. Ahnelt, E. Fernandez, O. Martinez, J. A. Bolea, and A. Kueber-Heiss,
Irregular s-cone mosaics in felid retinas. Spatial interaction with axonless horizontal revealed by cross-correlation,
Journal of the Optical Society of America A (JOSAA), vol. 17, pp. 580-588, March 2000. [ bib | .pdf ]
Related Publications:
-
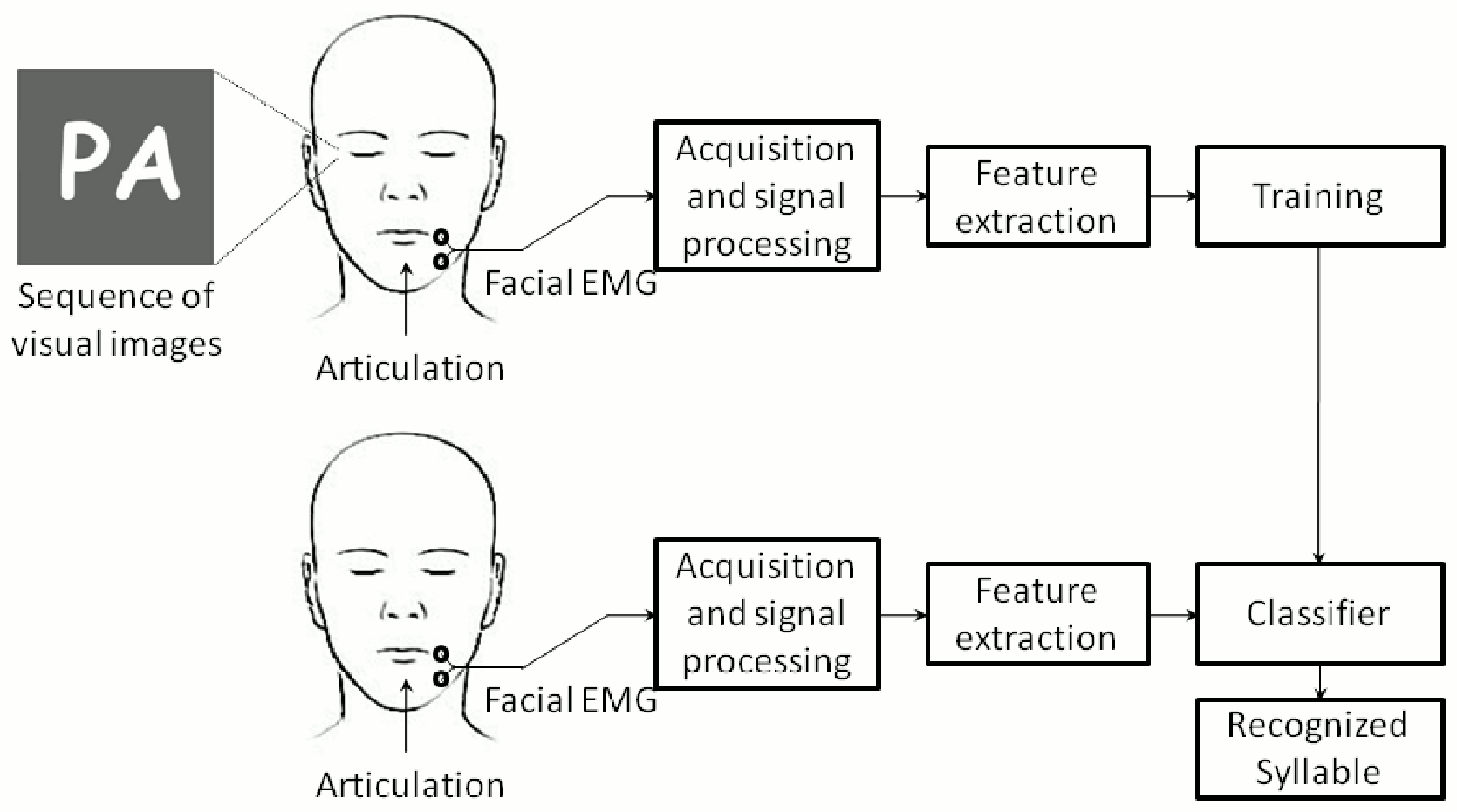
E. L. Larraz, O. M. Mozos, J. M. Antelis, and J. Minguez,
Syllable-based speech recognition using EMG,
in Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), (Buenos Aires, Argentina), pp. 4699-4702, September 2010. [ bib | .pdf ]
-
Strategic Information and Communication R\&D Promotion Programme (SCOPE)
Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, Japan.
Duration: 2012--2015.
-
Tracing everyday objects in indoor environment for robotic service to daily human life.
Japanese Government. Grant-in-Aid for JSPS Fellows.
Number: 22-00362. Duration: November 2010 - November 2012.
-
HYPER
Equipo de investigación en materia de neuroprotésica y neurorrobótica para la rehabilitación de trastornos motores en lesiones medulares, accidence cerebrovascular y parálisis cerebral.
Spanish Project. Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación. Consolider Ingenio. ID: CSD2009-00067. Duration: 2010-2014.
-
Neuro-control cognitivo de prótesis robóticas y de miembros humanos por estimulación eléctrica funcional para aplicaciones de rehabilitación.
Spanish project. Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación. ID: DPI2009-14732-C02-01. Duration: 2009-2011.
-
Exhibition Robots in FITUR 2009.
Two robots robots were developed to represent the city of Elche (Spain) at FITUR 2009, the largest tourism trade fair on the international circuit. The first robot represented the Lady of Elche, and the second robot represented a palm from Elche. The robots interacted with people visiting the exhibition.
-
Cognitive Systems for Cognitive Assistants - CoSy.
European Union FP6 IST Cognitive Systems Integrated project.
Call: FP6-2002-IST-2. Area: IST-2002-2.3.2.4.
ID: FP6-004250-IP. Duration: Sept 2004 - Aug 2008.The main goal of the project is to advance the science of cognitive systems through a multi-disciplinary investigation of requirements, design options and trade-offs for human-like, autonomous, integrated, physical (eg., robot) systems, including requirements for architectures, for forms of representation, for perceptual mechanisms, for learning, planning, reasoning and motivation, for action and communication.
-
Sistema de percepción visual móvil y cooperativo como soporte para la realización de tareas con redes de robots.
Spanish project. Programa Nacional del Plan Nacional de Investigación Científica, Desarrollo e Innovación Tecnológica 2004-2007. Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia.
ID: DPI2007-61197. Duration: 1/10/2007 - 30/09/2010.
-
Smart-Team.
The goal of this project is to develop an autonomous vehicle based the Smart car. The project was created as a cooperation between the Autonomous Systems Lab at EPFL, Lausanne, and the research group for Autonomous Intelligent Systems at ALU, Freiburg, to participate in the ELROB 2006 event, where 20 European teams demonstrated outdoor navigation technology.
[Technical Paper (pdf: 737k)]
-
Mecanismos de degeneracion, regeneracion y reparacion en un modelo experimental neurodegenerativo
Spanish project from Ministerio de Educacion y Ciencia. June 1999 - June 2000.